6 common signs and symptoms of angioedema

Angioedema is a distinctive medical condition that flares with sudden, localized swelling beneath the skin’s surface. This swelling primarily targets areas like the eyes, lips, hands, and feet, distinguishing it from other forms of swelling. It is caused by fluid buildup that impacts the subcutaneous and submucosal layers of tissues in the impacted region. In most cases, an allergic reaction is the leading cause of angioedema. Here are some common signs to look out for.
Pronounced swelling
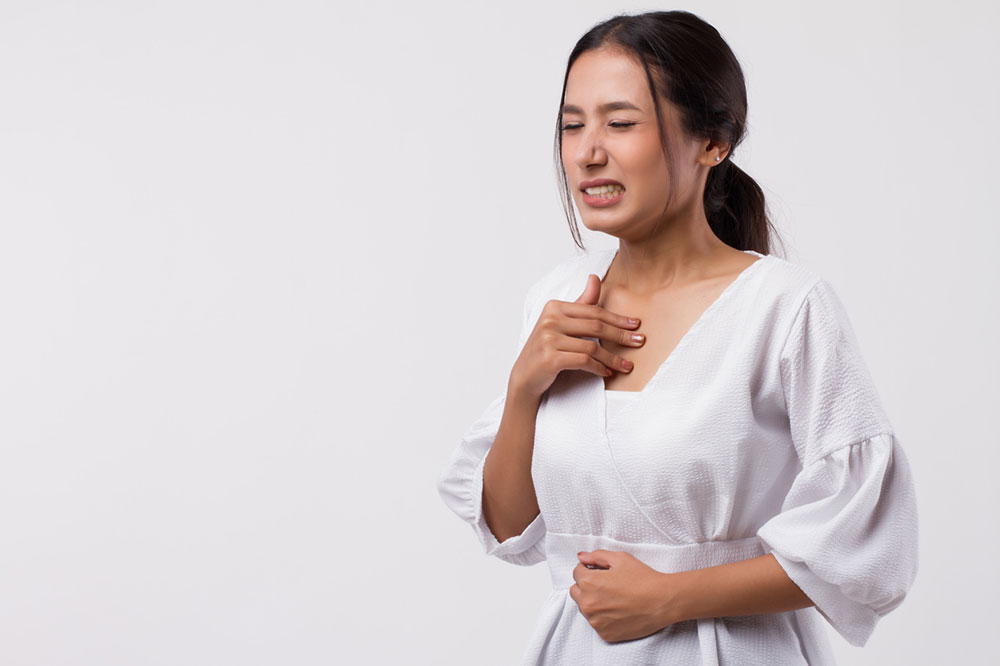
The most prominent symptom of angioedema is swelling, which occurs predominantly around the eyes, lips, cheeks, hands, and feet and manifests in deeper layers of the skin. Unlike the raised, itchy patches characteristic of hives, angioedema presents with a more profound, localized swelling. This swelling may cause discomfort, especially in areas where the skin is tightly stretched, such as around the eyes.
Swift and sudden onset
Angioedema distinguishes itself by its abrupt onset. Unlike other forms of swelling that may develop gradually, angioedema often emerges swiftly, sometimes within minutes. This rapid progression is a notable feature, underscoring the urgency of prompt recognition and intervention. The sudden nature of angioedema can be particularly alarming for individuals experiencing it for the first time, necessitating immediate attention.
Sensations of itching and discomfort
Individuals may also grapple with itching or discomfort in the affected areas. The intensity of this discomfort can vary from mild sensations to more acute discomfort, contributing to the overall distress associated with the condition. This itching and discomfort can be incredibly bothersome, prompting individuals to seek relief through various means, including topical treatments or prescriptions.
Targeted localization
Angioedema tends to affect areas characterized by looser connective tissue. As a result, the eyes, lips, cheeks, hands, and feet become common sites of occurrence. This specific distribution pattern sets angioedema apart from other forms, providing a critical clue for its identification. Understanding this characteristic localization can aid healthcare professionals in differentiating angioedema from other conditions and formulating an accurate diagnosis.
Variable duration of symptoms
The duration of angioedema can vary widely. In some cases, it may resolve within a few hours, while in others, it may persist for several days. Chronic angioedema, extending for six weeks or longer, is also possible. Discerning the duration of symptoms is instrumental in determining the appropriate course of action. Individuals experiencing chronic angioedema may face unique challenges in managing the condition over an extended period, necessitating ongoing monitoring and treatment.
Airway complications
In severe cases, angioedema can cause swelling of the airways and throat, leading to breathing difficulties and requiring immediate medical attention. Signs of airway involvement may include wheezing, difficulty swallowing, or a feeling of constriction in the throat. Prompt recognition of airway complications is critical in ensuring timely intervention and preventing potentially life-threatening situations.
Recurrence and management options
Angioedema can be an episodic or recurrent condition. Some individuals may endure multiple episodes over time. Understanding the triggers and potential underlying causes is vital in managing and preventing future occurrences.
Collaborative efforts between individuals and healthcare professionals can lead to tailored management strategies that enhance comfort and quality of life. A comprehensive approach to managing angioedema may involve identifying and addressing specific triggers, implementing preventive measures, and utilizing appropriate treatments to alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency of episodes.