Understanding blood donation – Eligibility criteria and benefits
Blood donation is an important part of healthcare, as it enables blood transfusion—a treatment option that can sustain and save lives. Data suggests that there are 11 million donors in the country, and over 11.5 million units of blood are collected in a year. Before the process begins, each donor is asked questions to assess the risk of bloodborne infections. Blood can be donated every 56 days and up to six times a year.
Eligibility criteria
One must meet the following criteria to be eligible to donate blood:
One must be fit and healthy on the day of the blood donation.
Depending on state law, one should be at least 16 or 17 years old. Some states enable legal minors to donate with parental approval. Although there is no legal maximum age, donor facilities may have different policies.
You must weigh a minimum of 110 pounds.
You must be able to pass the health history and physical exams.
Benefits
Blood donation can benefit both the recipients and the donors. Some of the key benefits of blood donation are:
Contributing to society: The only way to supplement blood loss is through donated human blood. Donating blood is seen as a noble cause, as it can help in the treatment of cancer, bleeding disorders, sickle cell anemia, and genetic blood abnormalities. According to the American Red Cross, donating one unit of blood might save the lives of up to three people.
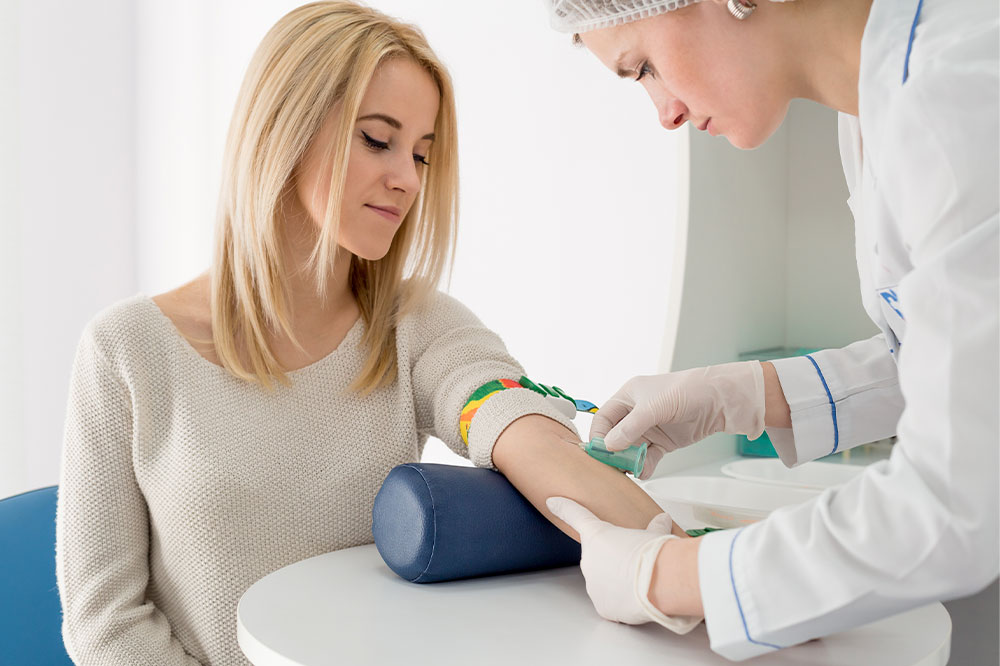
Health exam: Before donating blood, each donor goes through a quick health check and blood test. Although these tests are not extensive, they may be able to detect health conditions such as anemia or high or low blood pressure. The examination covers the donors’ iron levels, blood pressure, body temperature, and heart rate. One will not be able to donate blood if the test results indicate a problem in any of those parameters. However, the outcomes might serve as a starting point for treatment.
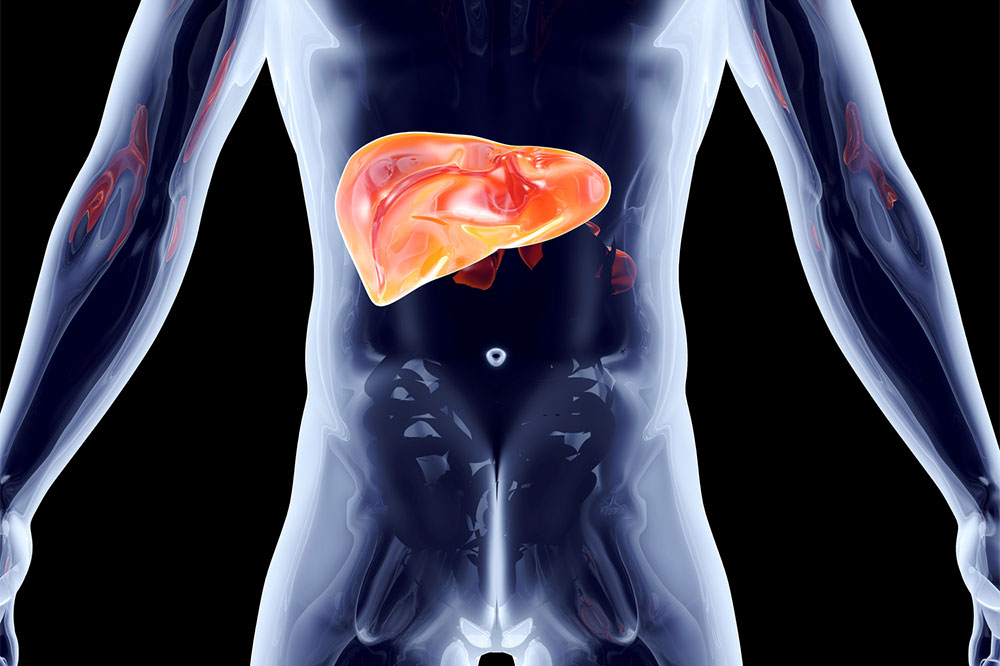
Prevents certain health issues: Blood donation can help reduce the risk of heart and liver damage caused by iron overload. An excessively iron-rich nutritional regimen can lead to conditions such as iron buildup in the heart and liver. Donating blood helps keep iron levels in check and reduces the risk of associated diseases.
Stimulates blood cell production: Following blood donation, the body works to make up for the blood loss. This stimulates the production of fresh blood cells, which helps maintain good health.
One should consult a doctor before donating blood to check for health issues or concerns. One should also follow a balanced meal plan for a few weeks before donating. Blood donations must be carried out at a blood bank, a hospital, or another setting with the presence of health professionals. On the day of the donation, one should have enough fluids to ensure hydration. Following such safety measures will help donors have a smooth and healthy experience.